Kubernetes with Kubespray
Requirements
- Ansible node: a Linux machine to run ansible (able to run in WSL or Docker but it’s not recommended)
- K8s nodes:
- Master nodes: 4GB RAM is recommended (2GB RAM will cause very low performance)
- Worker nodes: can start with 1CPU and 2GB RAM
You can setup a K8S cluster with only 1 node: master + worker (+ ansible)
Installation steps
Setup environments
- SSH connection: Ansible connects nodes over SSH, so the easy way is create the same user with public ssh key on all K8s nodes. You should use a golden image or template to create K8s nodes:
- Launch template or ARM template if you use cloud provider such as AWS, Azure
- VM template with on-premise hypervisor (Vshpere, Hyper-V, Citrix, ..)
- Cloud-init 🠈 I used this option, check this post Create Proxmox VM with Terraform (Cooming soon)
- Setup Kubespray: Install ansible and clone Kubespray repo
Prepare inventory
Static inventory
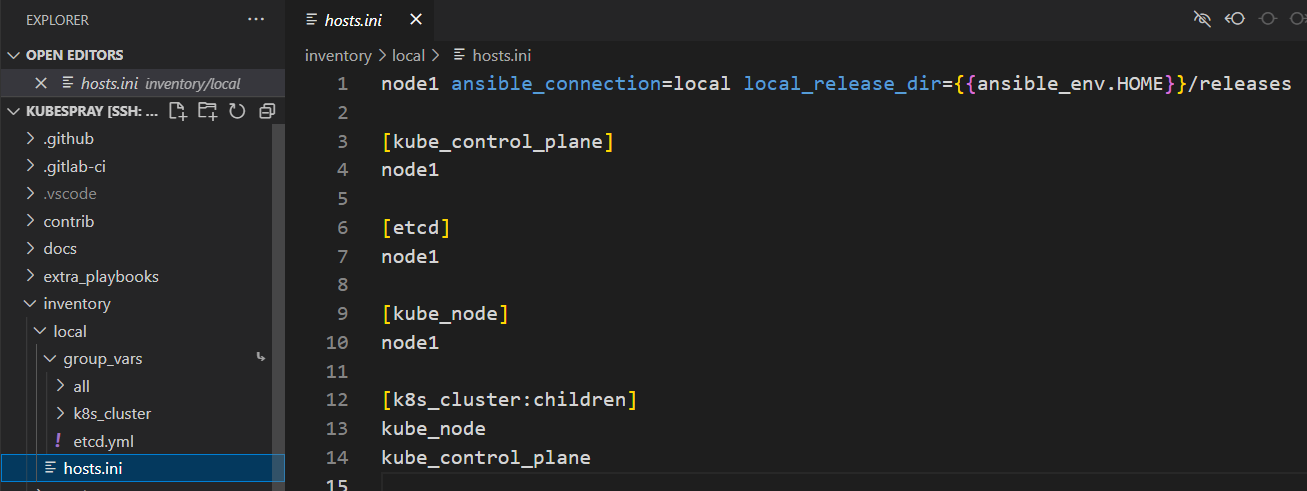
- You can use existing inventory file /inventory/local/hosts.ini to setup a “Single node cluster”
- Make a copy of
sampleinventory folder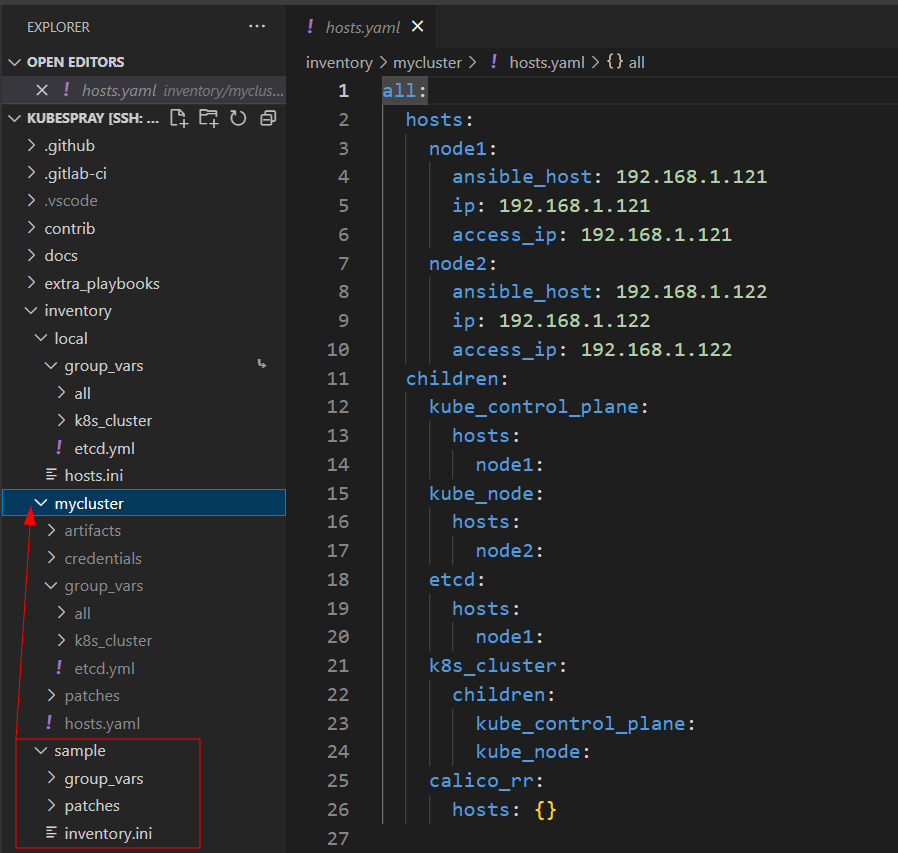
To get much information, visit these links: Kubespray inventory and Configurable Parameters in Kubespray
The inventory is composed of 3 groups:
- kube_node : list of kubernetes nodes where the pods will run.
- kube_control_plane : list of servers where kubernetes control plane components (apiserver, scheduler, controller) will run.
- etcd: list of servers to compose the etcd server. You should have at least 3 servers for failover purpose.
Addressing variables
- ip - IP to use for binding services (host var)
- access_ip - IP for other hosts to use to connect to. Often required when deploying from a cloud, such as OpenStack or GCE and you have separate public/floating and private IPs.
- ansible_default_ipv4.address - Not Kubespray-specific, but it is used if ip and access_ip are undefined
Dynamic inventory
- Inventory plugins are developed in Python, and there are many available plugins . Examples:
- amazon.aws.aws_ec2 – EC2 inventory source
- Todo
- community.general.proxmox – Proxmox inventory source
- Todo
- amazon.aws.aws_ec2 – EC2 inventory source
- Inventory scripts allow users to use other programming languages.
- Developing dynamic inventory
Configure cluster
There are many Configurable Parameters in Kubespray. You can find yaml files in folder inventory/mycluster/group_vars
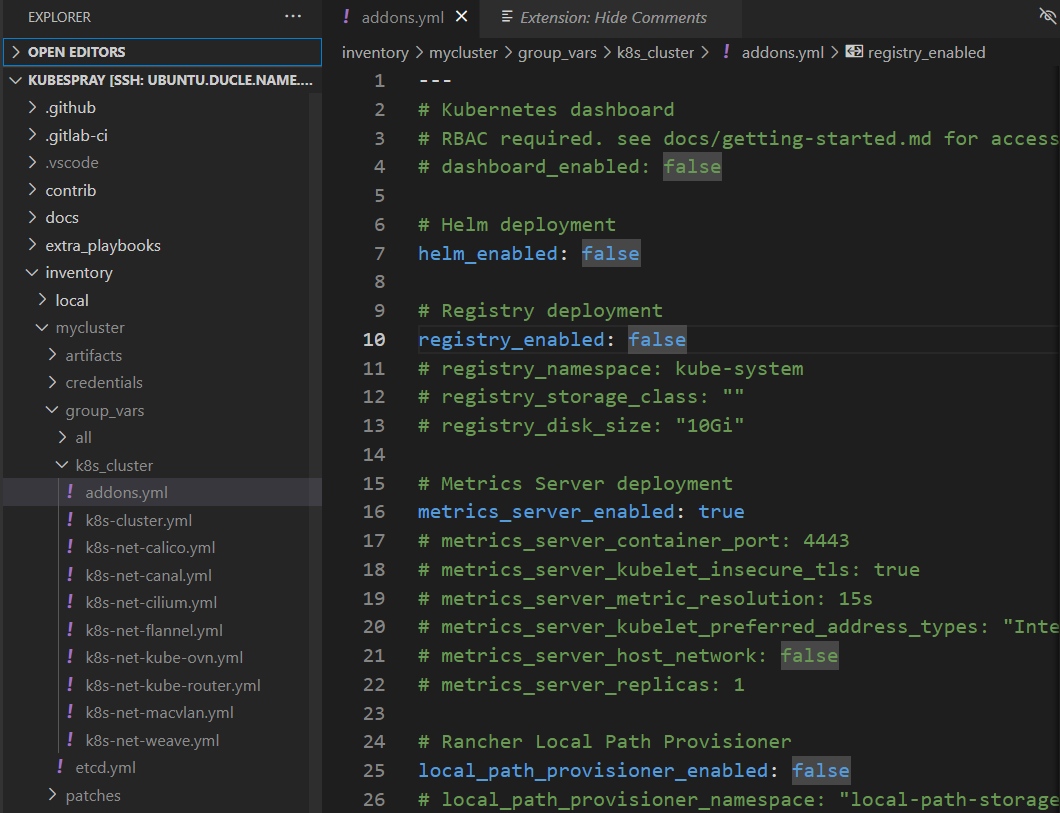
There are some custom parameters I usually use
#inventory/mycluster/group_vars/k8s_cluster/k8s-cluster.yml
kube_version: v1.25.5
kube_network_plugin: calico
kubeconfig_localhost: true
auto_renew_certificates: true#inventory/mycluster/group_vars/k8s_cluster/addons.yml
metrics_server_enabled: true
ingress_nginx_enabled: true
argocd_enabled: trueDeploy K8s cluster
Run ansible-playbook command to deploy your cluster.
$ ansible-playbook -i inventory/mycluster/hosts.yaml --become --become-user=root cluster.ymladmin.conf file to manage cluster with kubect command.
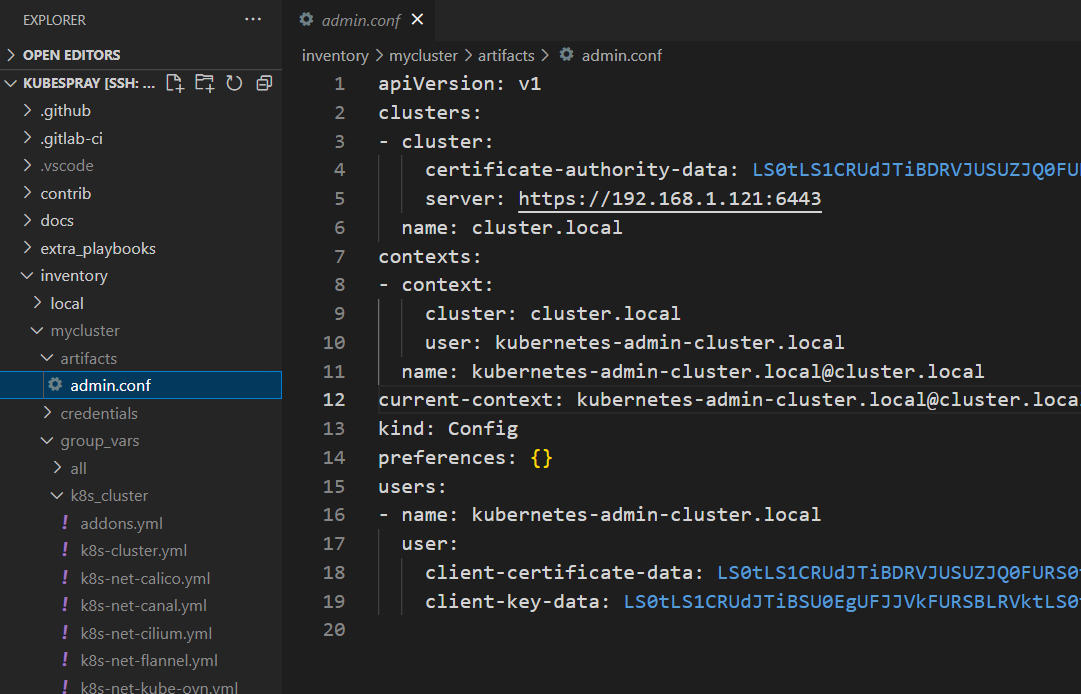
Documents
- Official document
- Installing Kubernetes with Kubespray on kubernetes.io
- If you need a step-by-step tutorial, just check out this post from my friend.
